Types
 Oregon white truffle (Tuber oregonense and T. gibbosum)
Oregon white truffle (Tuber oregonense and T. gibbosum)
Reasonably common in the Pacific Northwest from the west side of the Cascade Mountains to the coast from British Columbia to northern California. Tuber oregonense is generally found from October through February. Its exterior perideum is whitish when young, developing orangish-brown tints as it matures, and finally becoming orangish-brown overall. By February, most of the Tuber oregonense should be pretty mature and the T. gibbosum will just be getting started.
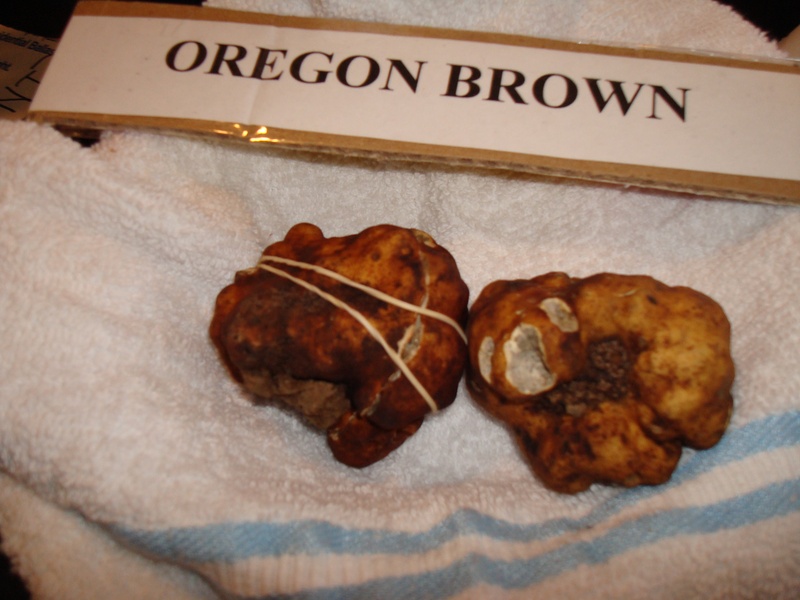

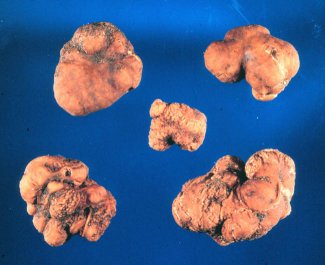
Oregon brown truffle (Leucangium brunneum)
The Oregon brown truffle was discovered by NATS members in the early 1990's. It grows in younger Douglas-fir forests in the Oregon Coast Range and western foothills of the Cascades. It has a reddish-brown exterior and a greyish mottled interior. When mature the odor can be quite garlicky.
 Oregon black truffle (Leucangium carthusianum, formerly Picoa carthusiana)
Oregon black truffle (Leucangium carthusianum, formerly Picoa carthusiana)
Less common than Oregon white truffles, Oregon blacks are larger (golf-ball to baseball size), and are often much deeper in the soil than Oregon whites (commonly 4-10" deep). They are very dark inside and out, and have a very pungent, earthy odor when ripe. Some equate the aroma to a strange mix of pineapple, port, mushrooms, rich soil, and chocolate. Looking like irregular lumps of coal, with white-veined flesh, the Oregon black truffle has a texture of moist Parmesan and ground almonds.

French black (Perigord) truffle (Tuber melanosporum)
Native to the oak forests of the Perigord region of central and southwest France, it is now widely cultivated in Spain, Australia, and the United States. The black perigord is among the most valuable of truffles at up to $1000/pound. It has a blue-black exterior when fresh, fading to brown-black with age and a pungent, earthy odor.
Italian white (Piedmont) truffle (Tuber magnatum) Considered by some (mostly the French) to be second best to the French black truffles, its cost can exceed that of the perigord. It is native to the foothills and mountains of northern and central Italy and southern Yugoslavia. They grow in conjuction with oak, hazel, poplar, and beech trees. The flesh is solid, light-coloured, and very brittle; it is not unheard of for a fresh truffle to shatter if dropped on the floor. Large specimens can weigh as much as a pound, but most are the size of large walnuts. The white truffle is slightly more perishable than its darker cousins, and the flavor and aroma diminishes within a week or two after harvest. The white truffle has a distinctive pepper edge and is often eaten raw. The skin is a dirty beige when fresh, turning a darker brown with age.
Considered by some (mostly the French) to be second best to the French black truffles, its cost can exceed that of the perigord. It is native to the foothills and mountains of northern and central Italy and southern Yugoslavia. They grow in conjuction with oak, hazel, poplar, and beech trees. The flesh is solid, light-coloured, and very brittle; it is not unheard of for a fresh truffle to shatter if dropped on the floor. Large specimens can weigh as much as a pound, but most are the size of large walnuts. The white truffle is slightly more perishable than its darker cousins, and the flavor and aroma diminishes within a week or two after harvest. The white truffle has a distinctive pepper edge and is often eaten raw. The skin is a dirty beige when fresh, turning a darker brown with age.
 Burgundy, or Summer truffle (Tuber aestivum, formerly Tuber uncinatum)
Burgundy, or Summer truffle (Tuber aestivum, formerly Tuber uncinatum)
Native to France, Italy, and Spain, the summer truffles are usually at their best in July, but can be found from May to October. They have a black exterior and off-white interior, and a relatively light scent. This truffle has been established on plantations in Sweden and New Zealand.
Tuscan truffle (Tuber borchii, formerly Tuber albidum)
Similar to the Italian white truffle in appearance, having a chestnut to muddy tan exterior and a softish interior equally divided between chocolate brown and white. The flavor can be distinctly garlicky.
Pecan (Texas) truffle (Tuber lyonii, formerly Tuber texense)
Pecan truffles (also called Texas truffles) are found from New Mexico to the gulf coast and eastern seaboard to the great lakes and eastern Canada. It is not limited to areas with pecan trees, but was named based on the habitat in which it was discovered.
 Chinese truffles (Tuber sinense, Tuber indicum, and Tuber himalayense)
Chinese truffles (Tuber sinense, Tuber indicum, and Tuber himalayense)
These are three distinct species found in South China, but pickers tend to lump them together as Chinese truffles. This is unfortunate since the flavor and quality vary from one species to another. First marketed in France in 1994, these truffles are now found in American restaurants at fairly reasonable prices, but their flavor and aroma do not come close to that of the French truffles, perhaps for the same reasons as Oregon white truffles (too many immature specimens). T. indicum is recognizable by its brown interior and very fine white veins. T. sinense has a dark brown interior with large ivory veins, and is said to be chewy and oily with a bitter aftertaste.

Desert truffles (Terfezia boudieri, Terfezia pfielii, Terfezia claveryi, and others)
Native to northern Africa and the Middle East, these truffles have been a staple for many nomadic tribes for millenia. Sometimes called the Lightning Truffle, they often fruit shortly after thunderstorms wet the desert.